1. struct
#include <iostream>
struct Dog {
int age;
double weight;
};
int main()
{
Dog coco; //struct 생략 가능
coco.age = 1;
coco.weight = 1.5;
std::cout << coco.age << " " << coco.weight << std::endl;
}c언어에서는 struct 도구라고 쓰고 c++언어 도그라고 써도 된다(생략 가능)
2. struct 대신 class로 변경 > 오류남
#include <iostream>
class Dog {
private:
int age;
double weight;
int getAge() {
return age;
}
void setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
};
int main()
{
Dog coco; //struct 생략 가능
coco.age = 1; //'Dog::age': private 멤버('Dog' 클래스에서 선언)에 액세스할 수 없습니다.
coco.weight = 1.5;
std::cout << coco.age << " " << coco.weight << std::endl;
}3. C와 C++ 차이점

아무것도 안쓰면 private이 기본
4. 정수(Integer) 클래스와 객체

class명 : Integer
객체명 : Val1(이렇게 만들지 않음), Val2
5. Dog 클래스
#include <iostream>
class Dog {
private:
int age;
double weight;
public:
int getAge() {
return age;
}
void setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
public:
double getweight() {
return weight;
}
void setweight(double a) {
weight = a;
}
};
int main()
{
Dog coco; //struct 생략 가능
coco.setAge(1);
coco.setweight(1.5);
std::cout << coco.getAge() << " " << coco.getweight() << std::endl;
}6. 클래스 멤버의 접근 권한

프라이벗 콜론은 안써도 됨 접근 속성이 프라이벗이 기본
7. Access modifiers

생략 가능한 기본 접근 속성
8. 클래스 멤버의 접근 권한
접근 속성이 3가지가 있다. 감출 땐 프라이티브 누구에나 줄 땐 퍼블릭 자식에만 열어주려면 protected
9. void

10. 함수 정의, 호출, 선언

11. 멤버함수를 클래스 안에서 정의
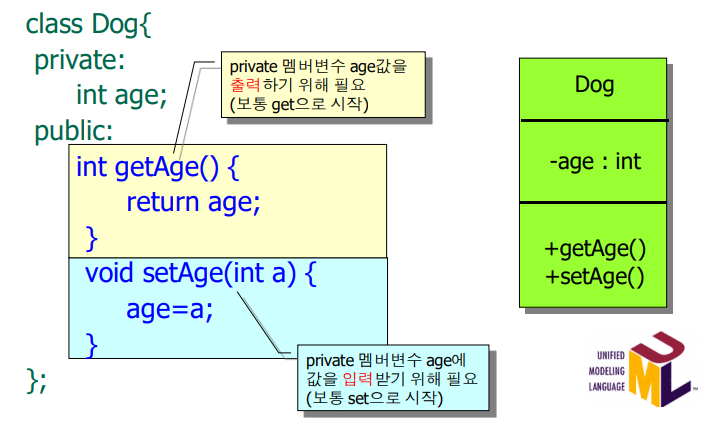
첫번째 칸 : 클래스 이름, 두번째 칸 : 변수, 세번째 칸 : 함수 / -프라이벗 +퍼블릭
12. Dog 클래스 다이어그램

13. 범위 지정 연산자(scope resolution operator) '::'

후속 변수 앞에 전역변수
14. using과 namespace


15. namespace
//aa.h
namespace AA
{
int add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
}
//bb.h
namespace BB
{
int add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y + 1;
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include "aa.h"
#include "bb.h"
int add(int x, int y) { return x + y + 2; }
int main()
{
std::cout << AA::add(1, 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << BB::add(1, 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << ::add(1, 2);//전역 namespace
return 0;
}16. 자동 inline 함수

클래스 내부에 만들게되면 자동으로 인라인함수가 된다. 속도가 빠르다
17. 정수(Integer) 클래스

18. Dog 클래스 수정
//수정 후
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge()
{
return age;
}
void setAge(int a)
{
age = a;
}
};
int main()
{
Dog happy; // Dog class의 happy객체 정의
happy.setAge(3); // ② age는 private멤버로 클래스 밖에서 접근 불가
cout << happy.getAge(); // ③ age는 전용멤버로 접근 불가
return 0;
}
C++ 강의 자료 참고했습니다.
'C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 12주차 상속(inheritance) (2) | 2023.11.23 |
|---|---|
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 11주차 함수중첩, 디폴트 인자 (0) | 2023.11.16 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 10주차 const동적 메모리 할당(new, delete) (6) | 2023.11.09 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 9주차 객체와 멤버 생성자 소멸자 this (0) | 2023.11.02 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 6주차 객체지향언어특징 클래스와객체 접근속성 (0) | 2023.10.12 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 5주차 함수 기억클래스 구조체 (2) | 2023.10.05 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 3주차 C문법 정리2 (0) | 2023.09.21 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 2주차 C문법 정리1 (0) | 2023.09.14 |



