1. 취업에서 필요한 기술스택
2. private(protected)과 public 멤버의 접근 방법
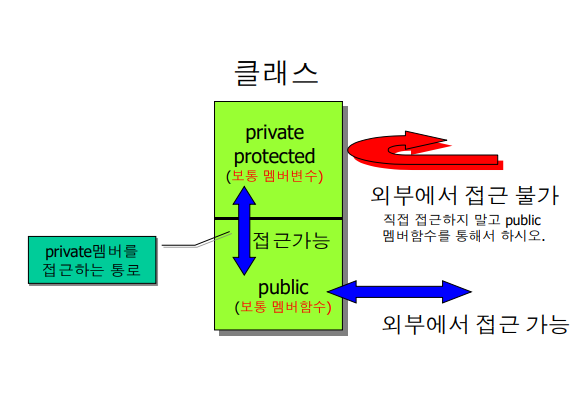
#include <iostream> // C++의 표준 입출력 라이브러리를 포함시킵니다.
class Dog { // "Dog"라는 이름의 클래스를 선언합니다.
private: // 이후에 나오는 멤버들은 private으로, 클래스 외부에서 직접 접근할 수 없습니다.
int age; // "age"라는 이름의 int형 멤버 변수를 선언합니다. 이 변수는 개의 나이를 저장합니다.
public: // 이후에 나오는 멤버들은 public으로, 클래스 외부에서 접근할 수 있습니다.
int getAge() { // "getAge"라는 멤버 함수를 선언하고 정의합니다. 이 함수는 개의 나이를 반환합니다.
return age; // age 멤버 변수를 반환합니다.
}
void setAge(int a) { // "setAge"라는 멤버 함수를 선언하고 정의합니다. 이 함수는 개의 나이를 설정합니다.
age = a; // 입력받은 값 a를 age 멤버 변수에 저장합니다.
}
};
int main() // 프로그램의 시작점인 main 함수를 선언하고 정의합니다.
{
Dog happy; // "Dog" 클래스의 객체인 "happy"를 선언합니다.
happy.setAge(3); // happy 객체의 나이를 3으로 설정합니다.
// happy.age = 3; // 이 코드는 에러입니다. "age"는 private 멤버이므로 직접 접근할 수 없습니다.
std::cout << happy.getAge(); // happy 객체의 나이를 출력합니다.
return 0; // 프로그램을 정상 종료합니다.
}3. 2번 소스의 멤버 함수를 class 밖으로 작성
#include <iostream>
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge();
void setAge(int a);
};
int Dog::getAge() {
return age;
}
void Dog::setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
int main()
{
Dog happy;
happy.setAge(3);
// happy.age = 3;
std::cout << happy.getAge();
return 0;
}4. 객체의 멤버 호출

5. 객체의 멤버 호출과 재사용 단위 : 오류 찾고 수정하기
//수정 전
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge();
void setAge(int a);
};
int Dog::getAge()
{
return age;
}
void Dog::setAge(int a)
{
age = a;
}
int main()
{
Dog happy; // Dog class의 happy객체 정의
Dog.age = 2; // ① Dog는 class
happy.age = 3; // ② age는 private멤버로 클래스 밖에서 접근 불가
cout << happy.age; // ③ age는 전용멤버로 접근 불가
return 0;
}
//수정 후
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge();
void setAge(int a);
};
int Dog::getAge() {
return age;
}
void Dog::setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
int main() {
Dog happy; // Dog 클래스의 happy 객체 정의
// Dog.age = 2; // ① Dog는 클래스, 클래스 자체에는 접근이 불가능
happy.setAge(3); // ② age는 private 멤버로 클래스 밖에서 접근 불가하므로 setAge() 함수를 통해 접근
cout << happy.getAge(); // ③ age는 private 멤버로 접근 불가하므로 getAge() 함수를 통해 접근
return 0;
}6. Dog클래스와 happy객체(인스턴스)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
double weight;
std::string name;
public:
int getAge() {
return age;
}
void setAge(int a) {
age = a;
}
double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
void setWeight(double w) {
weight = w;
}
std::string getName() {
return name;
}
void setName(std::string n) {
name = n;
}
void cry();
};
void Dog::cry() {
std::cout << "멍멍 \n";
}
int main()
{
Dog happy;
happy.setAge(3);
happy.setWeight(3.5);
happy.setName("해피");
cout << happy.getName() << "는 "
<< happy.getAge() << "살, "
<< happy.getWeight() << "kg입니다.\n";
happy.cry();
return 0;
}7. 많이 사용하는 문자열 관련 함수
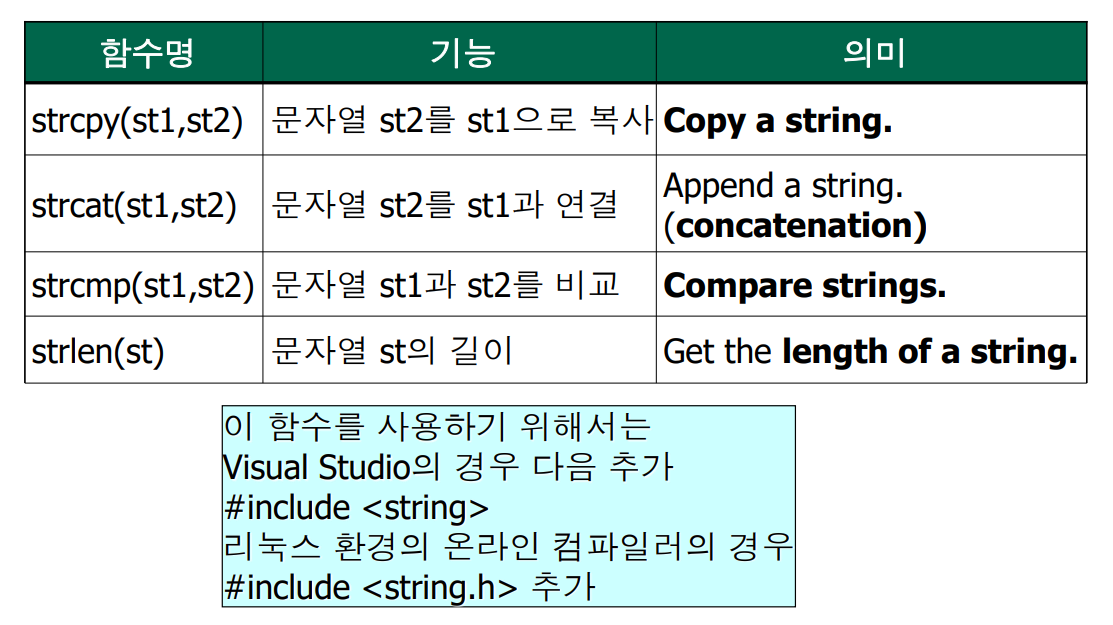
8. 배열 복사는 strcpy() 사용

9. string형은 대입하면 복사
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
std::string s1;
std::string s2 = "soft";
s1 = s2; //string형 복사는 그냥 대입
//strcpy(s1, s2);
std::cout << "s1=" << s1 << " s2=" << s2;
return 0;
}10. 문자, 문자열(const char* or std::string)리턴 자판기 함수
//문자
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char vending(int x)
{
if (x == 1) return 'A';
else return 'B';
}
int main()
{
cout << vending(1);
return 0;
}
//문자열 const char*
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const char* vending(int x)
{
if (x == 1) return "커피";
else return "유자차";
}
int main()
{
cout << vending(1);
return 0;
}
//문자열 std::string
#include <iostream>
std::string vending(int x)
{
if (x == 1) return "커피";
else return "유자차";
}
int main()
{
cout << vending(1);
return 0;
}문자열을 리턴할 때는 const char*(포인터)
11. 고양이 클래스1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //string.h
using std::cout;
class Cat {
private: //생략가능
int age;
char name[20]; // A
//const char *name; //B, 비추
public:
int getAge();
const char* getName();
void setAge(int a);
void setName(const char* pName);
};
int Cat::getAge()
{
return age;
}
void Cat::setAge(int a)
{
age = a;
}
void Cat::setName(const char* pName)
{
strcpy(name, pName); //A
//name=pName; //B, 주소 대입
}
const char* Cat::getName()
{
return name;
}
int main()
{
Cat nabi;
nabi.setName("나비");
nabi.setAge(3); //입력
cout << nabi.getName() << " 나이는"<<nabi.getAge()<<"살이다.";
return 0;
}12. 고양이 클래스2
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
//using namespace std; //C
class Cat {
private: //생략가능
int age;
std::string name; // C
public:
int getAge();
std::string getName();
void setAge(int a);
void setName(std::string pName);
};
int Cat::getAge()
{
return age;
}
void Cat::setAge(int a)
{
age = a;
}
void Cat::setName(std::string pName)
{
// strcpy(name, pName);
name = pName; //C
}
std::string Cat::getName()
{
return name;
}
int main()
{
Cat nabi;
nabi.setName("나비");
nabi.setAge(3); //입력
std::cout << nabi.getName() << " 나이는"<<nabi.getAge()<<"살이다.";
return 0;
}13. 객체 배열
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge() { return age; } //자동 inline함수
void setAge(int a) { age = a; } //자동 inline함수
};
int main()
{
int i;
Dog dd[5]; //Dog클래스형 객체배열 dd, 강아지 5마리
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
dd[i].setAge(i); //강아지 5마리 나이를 다 1로 하려면 dd[i].setAge(1);
cout << dd[i].getAge(); //01234
}
return 0;
}14. 포인터 객체
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int a) { age = a; }
};
int main()
{
Dog happy, * pd; //일반 객체 happy와 포인터 객체 pd, int x, *px;
pd = &happy; //px=&x;
happy.setAge(5); //일반 객체는 '.'으로 멤버를 접근
cout << happy.getAge() << pd->getAge(); //포인터 객체는 '->'로 멤버를 접근
pd->setAge(2);
cout << happy.getAge() << pd->getAge();
return 0;
}15. 생성자와 소멸자

16. 생성자(constructor)

17. c++, c#, 자바, 파이썬 생성자에 대해 설명
C++: C++에서 생성자는 클래스 이름과 동일한 이름의 메서드로, 객체가 생성될 때 자동으로 호출됩니다. 생성자는 멤버 변수의 초기화와 필요한 리소스의 할당 등을 담당합니다.
class Dog {
public:
Dog() { // 생성자
// 초기화 작업
}
};C#: C#에서도 생성자는 클래스 이름과 동일한 이름의 메서드로, 객체가 생성될 때 자동으로 호출됩니다. C#에서 생성자는 필드나 속성의 초기화, 메서드 호출 등을 수행할 수 있습니다.
public class Dog {
public Dog() { // 생성자
// 초기화 작업
}
}Java: Java에서 생성자는 클래스 이름과 동일한 이름의 메서드로, 객체가 생성될 때(new 키워드 사용) 자동으로 호출됩니다. 생성자는 멤버 변수의 초기화를 담당합니다.
public class Dog {
public Dog() { // 생성자
// 초기화 작업
}
}Python: Python에서 생성자는 __init__라는 특별한 메서드로, 객체가 생성될 때 자동으로 호출됩니다. 이 메서드는 멤버 변수의 초기화 등을 담당합니다.
class Dog:
def __init__(self): # 생성자
# 초기화 작업18. 초기화

19. 생성자의 특징

20. private멤버변수를 특정 값으로 초기화하는 생성자
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
Dog();
// Dog() { age = 1; }// 생성자 정의, Dog():age(1){ }, Dog():age{1}{ }
// Dog() : age(1) { };
// Dog() : age{ 1 } { };
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int a) { age = a; }
};
Dog::Dog() { //생성자
age = 1;
}
int main()
{
Dog happy; //happy객체가 생성되는 순간 생성자가 자동 호출됨
cout << happy.getAge();
return 0;
}21. private멤버변수를 특정 값으로 초기화하는 생성자
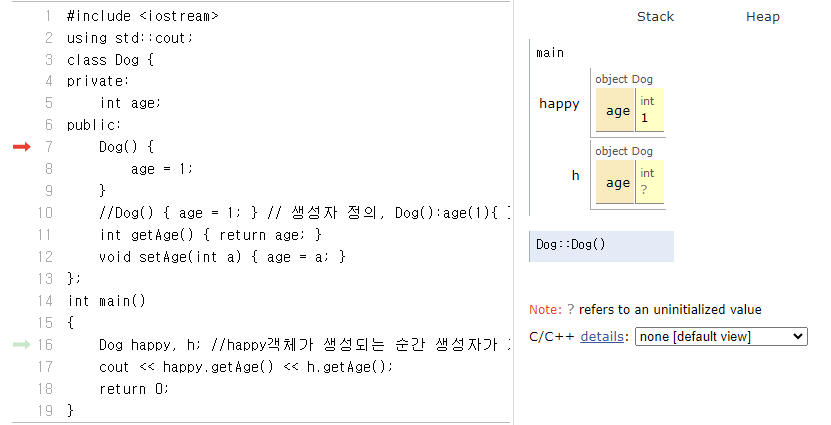
객체가 만들어질 때마다 자동으로 호출
22. C++에서 변수를 초기화하는 방법
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int x=1; //copy initialization,비추
int y(2);//direct initialization
int z{3};//Uniform initialization, C++11
int z1{};//Uniform initialization, 자동으로 0,C++11
std::cout << x << y << z << z1;
}23. 생성자의 매개변수가 있으면 객체 다음에 괄호 안에 매개변수로 넘어갈 값 입력
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
Dog(int a) { age = a; }
//Dog() { age = 1; }// 생성자 정의, Dog():age(1){ }, Dog():age{1}{ }
// Dog() : age(1) { };
// Dog() : age{ 1 } { };
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int a) { age = a; }
};
int main()
{
Dog happy(1), h(2); //happy객체가 생성되는 순간 생성자가 자동 호출됨
cout << happy.getAge() << h.getAge();
return 0;
}24. 소멸자 (destructor)

25. 객체가 소멸되면서 "소멸"이라고 출력되는 소멸자
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
Dog(int a) { age = a; }
~Dog() { cout << "소멸\n"; }
//Dog() { age = 1; }// 생성자 정의, Dog():age(1){ }, Dog():age{1}{ }
// Dog() : age(1) { };
// Dog() : age{ 1 } { };
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int a) { age = a; }
};
int main()
{
Dog happy{ 1 }, h{ 2 }; //happy객체가 생성되는 순간 생성자가 자동 호출됨
cout << happy.getAge() << h.getAge();
return 0;
}객체가 2개여서 소멸이 2번 출력
26. this 포인터

27. this 포인터 예시
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class Dog {
private:
int age;
public:
Dog(int age) { this->age = age; } //생성자
~Dog() { cout << "소멸\n"; } //소멸자
int getAge() { return age; }
void setAge(int age) {
this->age = age;
}
};
int main()
{
Dog happy{ 1 }, h{ 2 }; //happy객체가 생성되는 순간 생성자가 자동 호출됨
cout << happy.getAge() << h.getAge();
happy.setAge(5); cout << happy.getAge();
return 0;
}
C++ 강의 자료 참고했습니다.
'C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 13주차 overriding : 가상함수(virtual function)static (2) | 2023.11.30 |
|---|---|
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 12주차 상속(inheritance) (2) | 2023.11.23 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 11주차 함수중첩, 디폴트 인자 (0) | 2023.11.16 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 10주차 const동적 메모리 할당(new, delete) (6) | 2023.11.09 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 7주차 멤버의 접근 속성클래스와 객체 만들기 (2) | 2023.10.19 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 6주차 객체지향언어특징 클래스와객체 접근속성 (0) | 2023.10.12 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 5주차 함수 기억클래스 구조체 (2) | 2023.10.05 |
| [C++ 프로그래밍] 3주차 C문법 정리2 (0) | 2023.09.21 |



